Features and Advantages
- Remotely access ROS-based robots without VPN
- Use hands-free gesture control to navigate subroutines
- Visualize the live feed of a robot using AR glasses
- Run workspace-specific algorithms using robots
- Customize interfaces and gestures for operation
- Enhance worker safety through robotic teleoperation
- Store and visualize digital notes on any object
- Control multiple IoT robots through spoken commands
- Pull up work orders and video tutorials in AR glasses
- Monitor warehouses or lab spaces anywhere in the world
Use-Cases
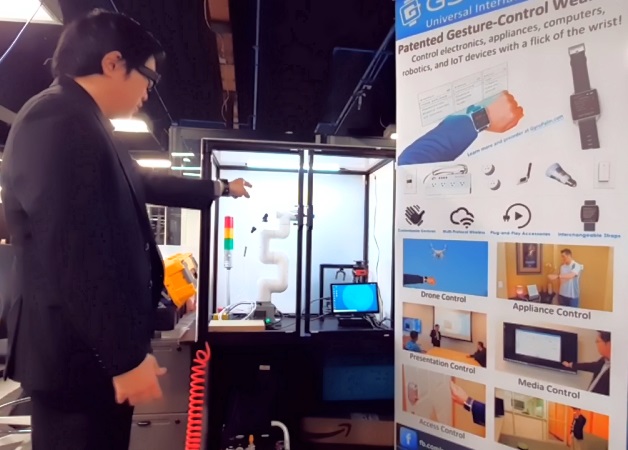

In the manufacturing industry, speed, accuracy, and synchronization are crucial for optimizing output. GyroPalm VIMPAACT revolutionizes the traditional manufacturing process by introducing smart, gesture-based command execution across multiple robotic systems and objects. By using QR codes and Aruco tags for contextual referencing, VIMPAACT makes it possible for users to switch seamlessly between different robotic interfaces, thereby enabling users to coordinate multiple machines and execute complex routines swiftly and effectively. Users to not need to hold a laptop or have any prior programming experience to use this framework. From pick and place routines on a robotic arm, to autonomous robotic maneuvers, GyroPalm VIMPAACT serves a critical purpose to be the interface that ensures safety, compliance, and coordination in the workplace.
A key use-case is in inventory management, where the GyroPalm VIMPAACT can greatly enhance efficiency. Our team has created proven workflows in object counting, dimension measuring, item sorting. In a large warehouse filled with a vast number of items, quickly identifying and tracking each product can be a daunting task. With the application of VIMPAACT, users can instantly tag, manage, and inventory objects, leading to significant time savings and improved accuracy. Using the GyroPalm Spectrum package, which comprises the GyroPalm Encore wearable and Vuzix Blade 2 AR glasses, these tasks can be executed hands-free, improving the ease, convenience, and pace of the inventory management and fulfillment process. The key strength of VIMPAACT is its ability to recognize and interact with objects in spaces ranging from a couple sqft to a large 30,000+ sqft facility.
Hardware
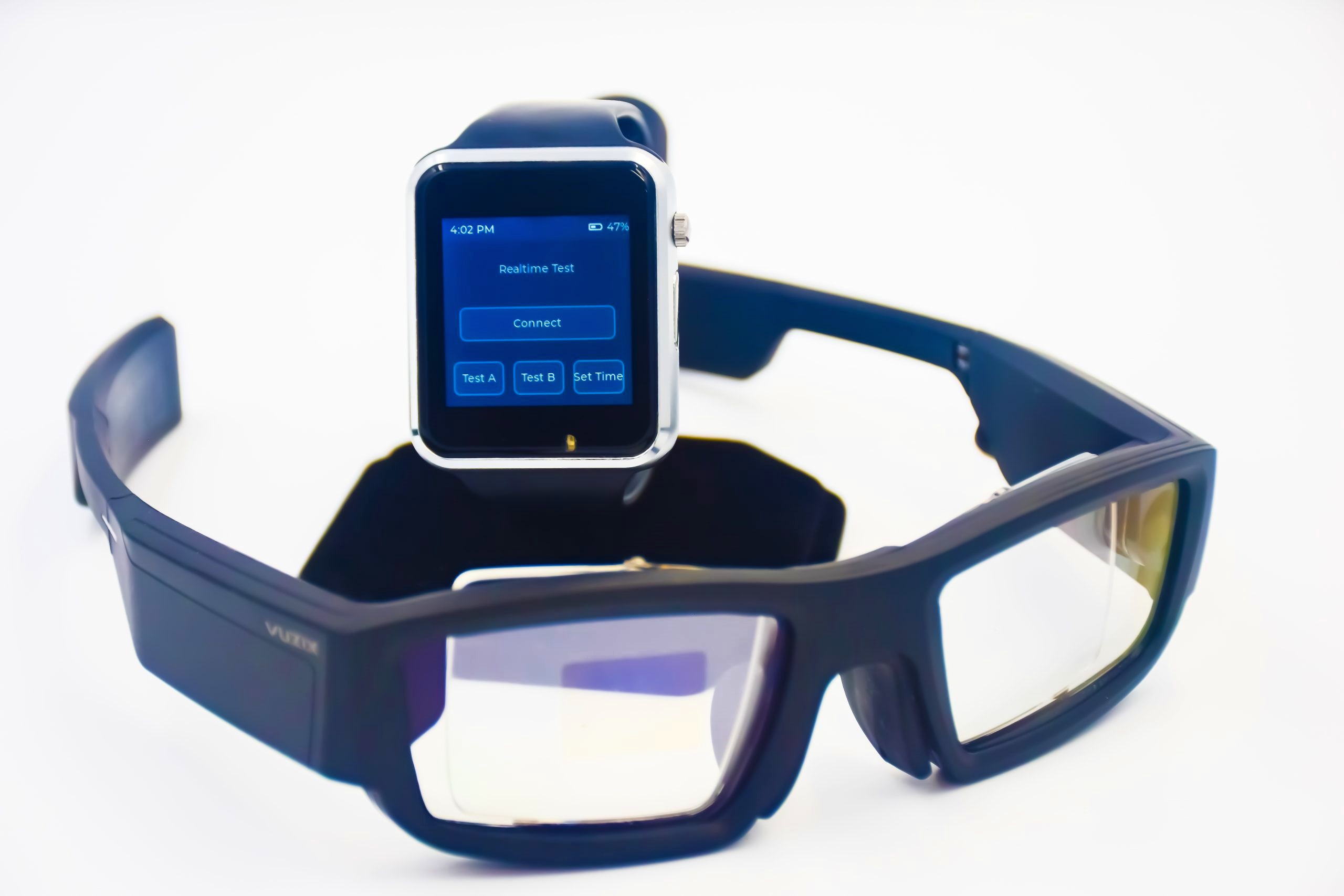

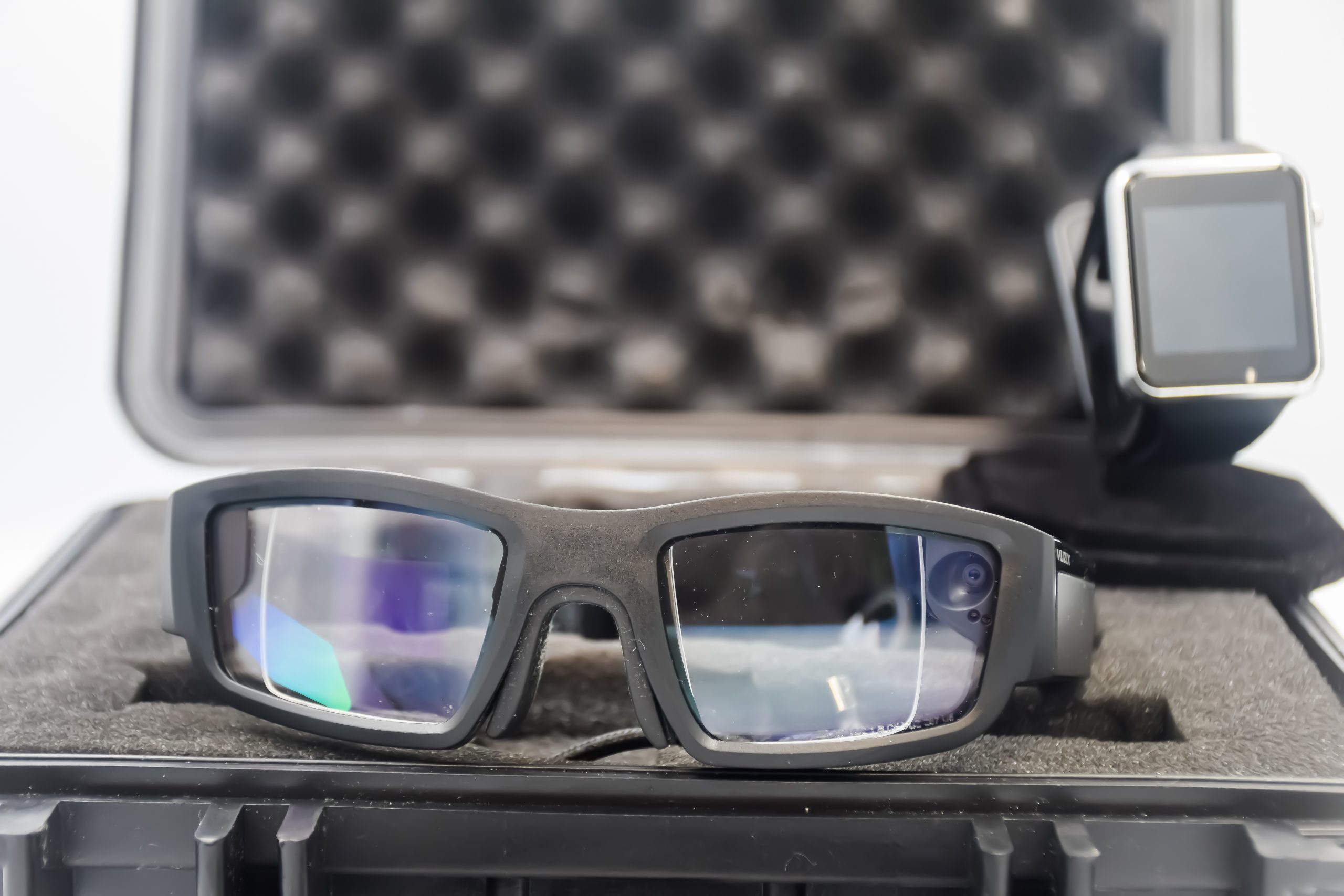
The VIMPAACT framework is designed to seamlessly connect workers to robots and machines through innovative wearables that can detect human gestures as well as display realtime information in front of the user. The interfaces is seamless and easy to activate while being unobtrusive whenever a user is not performing queries (i.e. using hands for another activity or speaking to another person). To accomplish this, we present the GyroPalm Spectrum package which comprises the GyroPalm Encore wearable and the flagship Vuzix Blade 2 AR glasses. Both wearables are wirelessly synchronized through the VIMPAACT framework and have edge-based capabilities to minimize false-positive detections. Additionally, a weatherproof industrial case with self-contained dual magnetic charger is provided with each set of GyroPalm Spectrum wearables. This enables the wearables to last a full day on the field without the need for constantly plugging into an AC adapter.


Protocol
The VIMPAACT protocol aims to expedite and enhance the following routines that are normally performed by human workers in the industry: Performance, Measurement, Inventory. The protocol starts with a dynamic QR code that contains 10 unique alphanumeric characters which is associated to a set of JSON characteristics. These characteristics defines the properties of an object (i.e. a sensor, actuator, robot, or item). Depending on those properties, a dynamic menu will be shown to the end-user via the AR glasses. The user can select actions to perform or dismiss this menu by performing subtle gestures using the GyroPalm Encore. While navigation can be performed with swipe gestures on the Vuzix Blade 2 glasses, the on-screen navigation is significantly expedited by using GyroPalm's customizable gestures. A dynamic QR code can contain characteristics that include a combination of Performance, Measurement, and Inventory routines.
Performance goals include actions that can be performed in a laboratory or facility environment with respect to a robot's working envelope. In one embodiment, an autonomous mobile robot (AMR) is driven from Point A to Point B when a user gazes at a specific pallet and does a hand-wave gesture. In another embodiment, a user makes a 6 DOF robotic arm perform several tasks by looking at various objects performing related gestures.
Measurement goals involve use-cases where one or more sensors are displayed to one or more VIMPAACT users through AR headsets. Sensors may include one or more of the following: thermistor, infrared (IR) camera, time of flight (ToF) sensor, photoresistor, PIR motion sensor, volt meter, amp meter, speedometer, spectrometer, pressure sensor, load sensor, etc. The values of one or more sensors are streamed and processed in realtime through the AR headset after a user gazes at the QR code attached to said sensor(s) and performs a gesture on the GyroPalm Encore. Gesture performance is necessary to ensure reliable hands-free operation.
Inventory goals involve the management and fulfillment of inventory in a production environment. Inventory tasks include routines normally performed by the shipping department of most enterprise companies, such as logging, tagging, box measurement, label creation, and locating items dynamically sorted in a warehouse. Inventory goals may also include tracking the lifecycle of returned or refurbished inventory, which often requires additional notes and tagging. As physical items get transported and handed to other personnel, VIMPAACT can help ensure that critical notes and messages are delivered to handlers or operators properly.
Usage Workflow
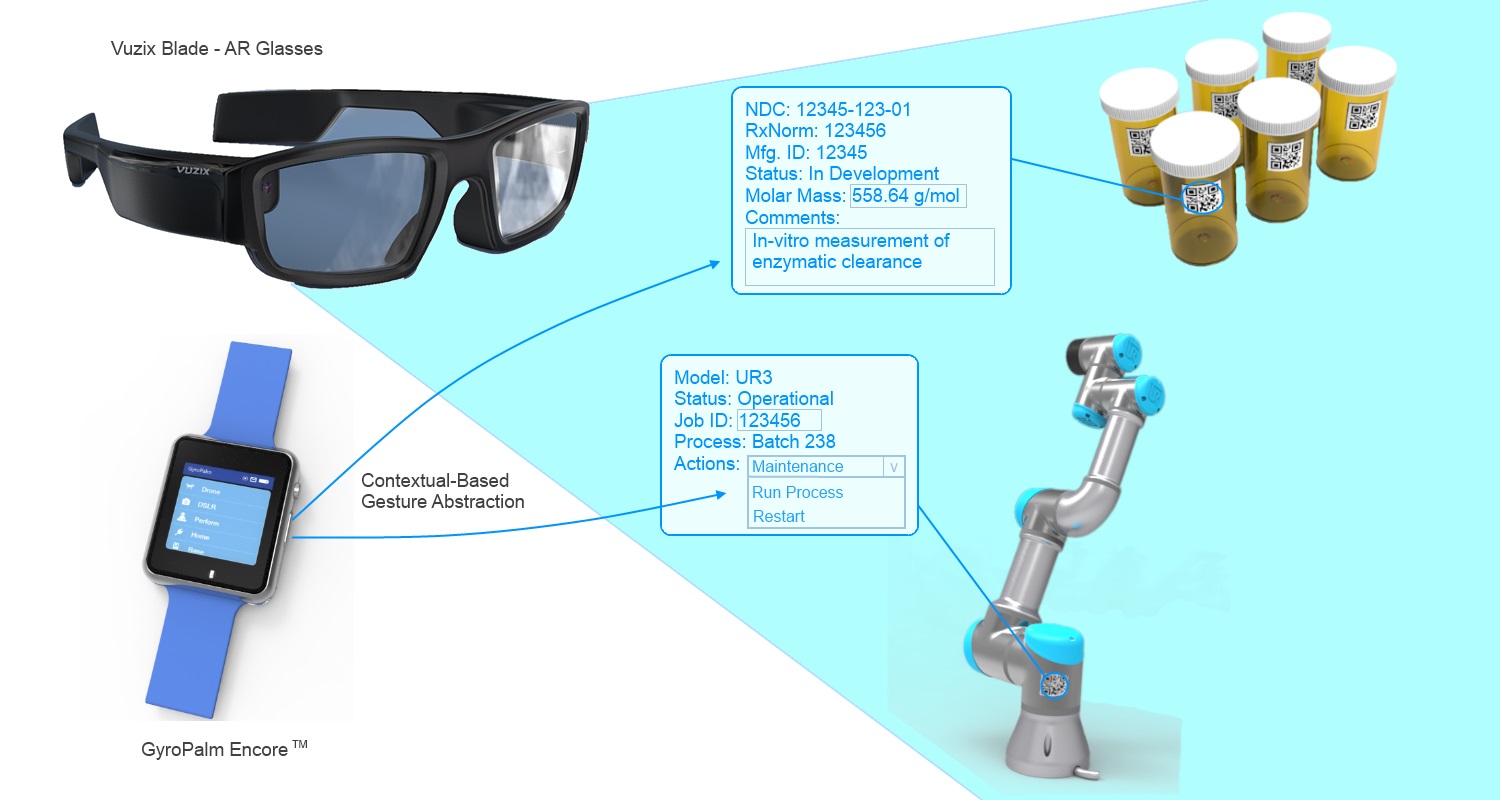
The VIMPAACT framework is designed with GyroPalm's Encore wearable in mind, which is to wireless connect the wearable to an AR headset that can be used anywhere in the field. The AR headset is expected to have a resolution of at least 300x300 pixels, camera for QR code scanning, and a capability to view HTML content as well as stream videos using WiFi. The GyroPalm Encore is expected to send data to the AR headset through WiFi or Bluetooth Low Energy. As shown in the illustration, when a user comes in proximity with a fiducial marker such as an Aruco tag or QR code, the user can perform an activation gesture (such as a double-snap) using the GyroPalm Encore to capture and decode the contents of the tag, in which the VIMPAACT protocol will be used to determine the JSON characteristics of the object, and display the relevant interface(s). The user can perform subsequent gestures (e.g. swipes, flicks, etc) under the context that these gestures are mapped to the respective commands of the target interface (i.e. controlling a robot, performing measurement, etc). In some instances, the user can also perform human spoken commands to instruct the robot to move to a specific location.
About
GyroPalm VIMPAACT is an NSF supported project. The GyroPalm Spectrum package (which runs the VIMPAACT framework) has won the "2023 Best Innovation-Wearable Award" in Sensors Converge EXPO, which is North America's largest Electronics Event for Design Engineers. VIMPAACT stands for Virtual Interfaces using Multi-Protocol Augmented-Reality Activation-based Control Transfer. The inventor and principal investigator is Dominick Lee, who owns different patents from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and graduated from Purdue University, a top ten U.S. university in technology. Dominick is an avid inventor and programmer who has more than 15 years of experience working with cloud/web development, mechatronics, and robotics solutions. He has been leading teams of Purdue scientists, scholars, and researchers on different GyroPalm R&D projects.
If you are interested in using GyroPalm VIMPAACT for your business, please feel free to contact us at dlee(@)gyropalm.com with your inquiry, or schedule a demo to learn more.
